Gaseous fuels - POLES: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Hydrogen == | == Hydrogen == | ||
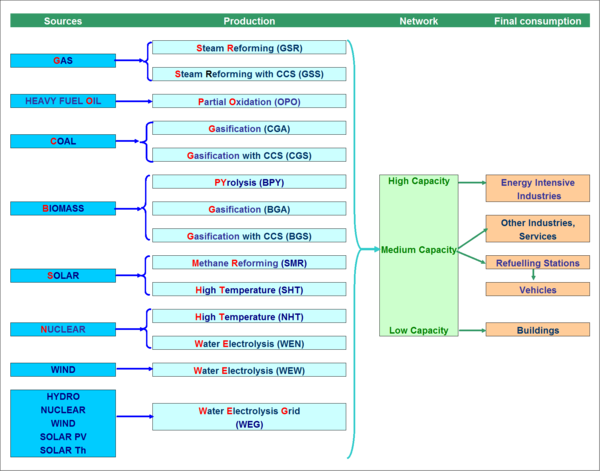
The | The model uses a complete module to represent hydrogen production (14), transport and use in various sectors: transport (fuel cells or thermal use), but also in stationary uses in industry and buildings (fuel cells or blending with natural gas). Water electrolysis from grid is coupled with the electricity load curve (hydrogen is produced preferentially during base load). | ||
<figure id="fig:POLES_8"> | <figure id="fig:POLES_8"> | ||
[[File:36405535.png|none|600px|thumb|<caption>The hydrogen module in POLES</caption>]] | [[File:36405535.png|none|600px|thumb|<caption>The hydrogen module in POLES</caption>]] | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
Hydrogen in the energy system in particular has been the subject of studies with the model[[CiteRef::EC 2006]]. | |||
Latest revision as of 12:51, 3 February 2017
| Corresponding documentation | |
|---|---|
| Previous versions | |
| Model information | |
| Model link | |
| Institution | JRC - Joint Research Centre - European Commission (EC-JRC), Belgium, http://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/. |
| Solution concept | Partial equilibrium (price elastic demand) |
| Solution method | SimulationRecursive simulation |
| Anticipation | Myopic |
Gas
Natural gas domestic production and imports directly supply gas for consumption. Additional gas production can come from:
- Urban waste methane recovery:
- Underground coal methane recovery
- Gas production fugitive emissions recovery
- Coke oven gas is captured in the final energy demand of the iron and steel sector
All three are determined by the effect of carbon pricing on the relevant emissions source.
Hydrogen
The model uses a complete module to represent hydrogen production (14), transport and use in various sectors: transport (fuel cells or thermal use), but also in stationary uses in industry and buildings (fuel cells or blending with natural gas). Water electrolysis from grid is coupled with the electricity load curve (hydrogen is produced preferentially during base load).
<figure id="fig:POLES_8">
</figure>
Hydrogen in the energy system in particular has been the subject of studies with the modelEC 2006.