Spatial dimension - REMIND-MAgPIE: Difference between revisions
Laura Delsa (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Laura Delsa (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
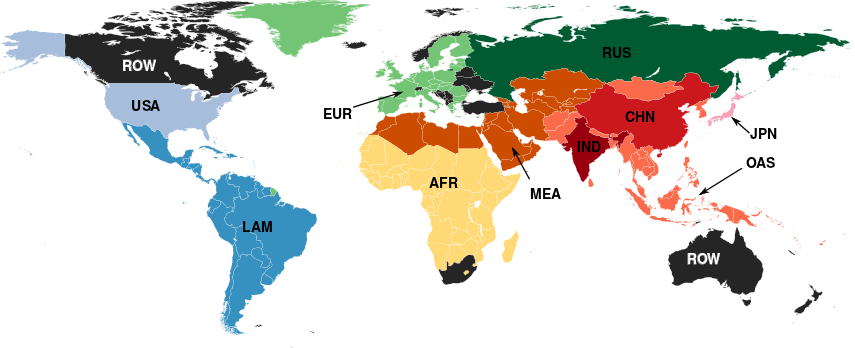
REMIND is a multi-regional model of global coverage, that divides the world into 11 regions (Figure 2). There are 5 individual countries (CHN - China; IND - India; JPN - Japan; USA - United States of America; and RUS - Russia) and 6 aggregated regions (AFR - Sub-Saharan Africa excluding Republic of South Africa; EUR - Members of the European Union; LAM - Latin America; MEA - including countries from the Middle East, North Africa, and central Asia; OAS - other Asian countries mainly located in South East Asia; and ROW - the rest of the world including Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Norway, and the Republic of South Africa). | REMIND is a multi-regional model of global coverage, that divides the world into 11 regions (Figure 2). There are 5 individual countries (CHN - China; IND - India; JPN - Japan; USA - United States of America; and RUS - Russia) and 6 aggregated regions (AFR - Sub-Saharan Africa excluding Republic of South Africa; EUR - Members of the European Union; LAM - Latin America; MEA - including countries from the Middle East, North Africa, and central Asia; OAS - other Asian countries mainly located in South East Asia; and ROW - the rest of the world including Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Norway, and the Republic of South Africa). | ||
REMIND represents explicitly trade in the composite good (aggregated output of the macro-economic system), primary energy carriers (coal, gas, oil, biomass, uranium), and in the case of climate policy, emissions allowances (cf. Section | REMIND represents explicitly trade in the composite good (aggregated output of the macro-economic system), primary energy carriers (coal, gas, oil, biomass, uranium), and in the case of climate policy, emissions allowances (cf. Section Trade). | ||
Global learning curves represent endogenous technological change through learning-by-doing for wind and solar power, as well as electric and fuel cell vehicle technologies. The spillovers among regions caused by this global learning are not internalized in the non-cooperative market solution, whereas in the socially optimal cooperative solution they are. | Global learning curves represent endogenous technological change through learning-by-doing for wind and solar power, as well as electric and fuel cell vehicle technologies. The spillovers among regions caused by this global learning are not internalized in the non-cooperative market solution, whereas in the socially optimal cooperative solution they are. | ||
Revision as of 20:43, 19 October 2016
| Corresponding documentation | |
|---|---|
| Previous versions | |
| Model information | |
| Model link | |
| Institution | Potsdam Institut für Klimafolgenforschung (PIK), Germany, https://www.pik-potsdam.de. |
| Solution concept | General equilibrium (closed economy)MAgPIE: partial equilibrium model of the agricultural sector; |
| Solution method | OptimizationMAgPIE: cost minimization; |
| Anticipation | |
REMIND is a multi-regional model of global coverage, that divides the world into 11 regions (Figure 2). There are 5 individual countries (CHN - China; IND - India; JPN - Japan; USA - United States of America; and RUS - Russia) and 6 aggregated regions (AFR - Sub-Saharan Africa excluding Republic of South Africa; EUR - Members of the European Union; LAM - Latin America; MEA - including countries from the Middle East, North Africa, and central Asia; OAS - other Asian countries mainly located in South East Asia; and ROW - the rest of the world including Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Norway, and the Republic of South Africa).
REMIND represents explicitly trade in the composite good (aggregated output of the macro-economic system), primary energy carriers (coal, gas, oil, biomass, uranium), and in the case of climate policy, emissions allowances (cf. Section Trade).
Global learning curves represent endogenous technological change through learning-by-doing for wind and solar power, as well as electric and fuel cell vehicle technologies. The spillovers among regions caused by this global learning are not internalized in the non-cooperative market solution, whereas in the socially optimal cooperative solution they are.
Figure 2. Regional definitions used in the REMIND model.