Uranium and other fissile resources - COFFEE-TEA: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
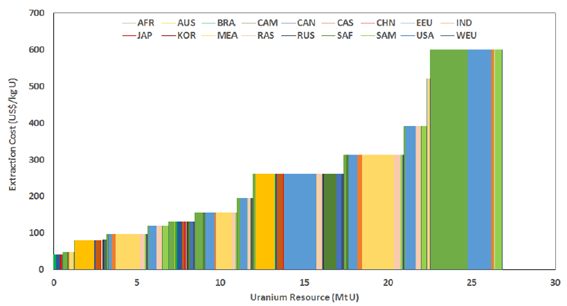
The estimates available in the literature for uranium resources are a lot more comprehensive and agreeable then that of oil and gas due to the national and international interest in mapping the location and accessibility of the nuclear resources, due to risk of exposure to natural radiation and potential proliferation of non-energetic nuclear technologies. For instance, | The estimates available in the literature for uranium resources are a lot more comprehensive and agreeable then that of oil and gas due to the national and international interest in mapping the location and accessibility of the nuclear resources, due to risk of exposure to natural radiation and potential proliferation of non-energetic nuclear technologies. For instance, [[CiteRef::iaea2014]] and other related literature provide a summary of national reports, which includes resource assessment of natural uranium. All these studies used the IAEA classification for uranium resources [[CiteRef::iaea2014]]. The resources are divided into two aspects, extraction costs and resource nature, as shown in <xr id="fig:Uranium"/>. | ||
<figure id="fig:Uranium"> | <figure id="fig:Uranium"> | ||
[[File:uranium.png|600px|thumb|<caption>Global supply curve for uranium</caption>]] | [[File:uranium.png|600px|thumb|<caption>Global supply curve for uranium</caption>]] | ||
</figure>. | </figure>. | ||
Revision as of 04:10, 3 August 2019
| Corresponding documentation | |
|---|---|
| Previous versions | |
| Model information | |
| Model link | |
| Institution | COPPE/UFRJ (Cenergia), Brazil, http://www.cenergialab.coppe.ufrj.br/. |
| Solution concept | General equilibrium (closed economy) |
| Solution method | The COFFEE model is solved through Linear Programming (LP). The TEA model is formulated as a mixed complementary problem (MCP) and is solved through Mathematical Programming System for General Equilibrium -- MPSGE within GAMS using the PATH solver. |
| Anticipation | |
The estimates available in the literature for uranium resources are a lot more comprehensive and agreeable then that of oil and gas due to the national and international interest in mapping the location and accessibility of the nuclear resources, due to risk of exposure to natural radiation and potential proliferation of non-energetic nuclear technologies. For instance, iaea2014 and other related literature provide a summary of national reports, which includes resource assessment of natural uranium. All these studies used the IAEA classification for uranium resources iaea2014. The resources are divided into two aspects, extraction costs and resource nature, as shown in <xr id="fig:Uranium"/>.
<figure id="fig:Uranium">
</figure>.